Structure of the skin (epidermis)
The skin is made up of three major parts: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue, each of which plays an important role.
Let's look at them in order from the top.
skin structure
- epidermis
- dermis
- subcutaneous tissue
The skin is divided into three layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue.
epidermis
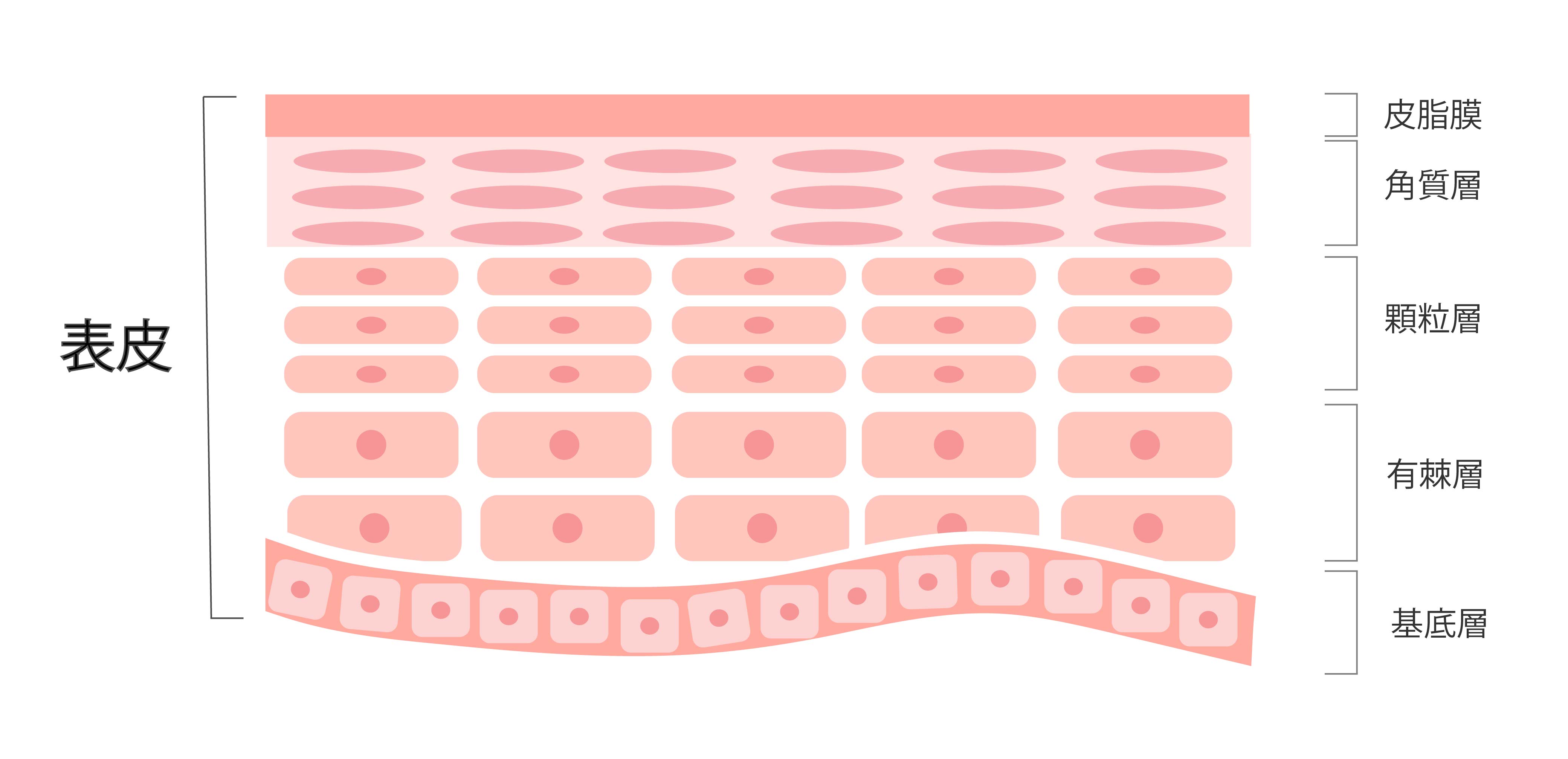
The epidermis is about 2 mm thick on average , and from the top
④ stratum corneum,
③granular layer,
② Spinous layer
① called the basal layer
It consists of four layers.
■ Epidermal turnover
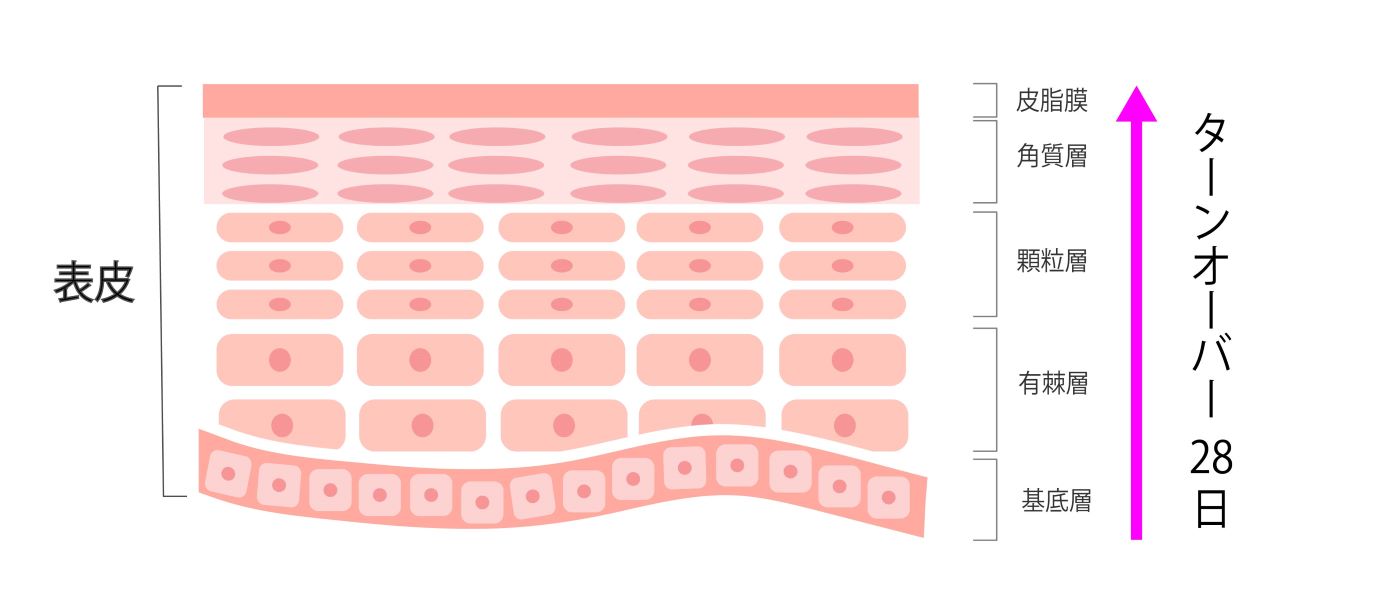
Cells of the epidermis (epidermal keratinocytes) are produced in ① the basal layer, and when new cells are born, the previous cells are pushed out, and gradually rise upwards → ② stratum spinosum → ③ stratum granulosum → ④ stratum corneum. I'll go.
Cells born in the basal layer climb up to the stratum corneum, and the cells that reach the top (the stratum corneum) usually turn into red and peel off within 28 days. This is called epidermal turnover.
① basal layer → ② spinous layer → ③ granular layer → ④ stratum corneum = 28 days!
■Composition of the epidermis
① Basal layer:

Vertically long basal cells are lined up and produce new keratinocytes.
| > Tips) Melanocytes are also located here and synthesize the pigment (melanin pigment) that protects the skin from ultraviolet rays. However, if the melanin pigment is not completely turned over due to aging or other causes, the pigment will remain on the skin and cause age spots. |
② Spinous layer:

Cells born in the basal layer become spinous cells in this layer, forming a layer (stratum spinosum). This layer receives oxygen and nutrients from the dermis, and also synthesizes proteins that form the stratum corneum and the granular layer that emerges in the skin.
③ Granular layer:

Cells that were in the spinous layer rise up and change shape to flattened cells (granule cells). Two to three layers of these cells overlap to form the granular layer. The proteins that make up the granule cells are then broken down into amino acids in the stratum corneum, which becomes the main component of NMF (natural moisturizing factor).
④Stratum corneum:

Cells that emerge from granule cells lose their nuclei and become stratum corneum cells. These stratum corneum cells overlap in 10 to 20 layers to form the last layer (the stratum corneum). This layer contains NMF (natural moisturizing factor) and intercellular lipids , which keep the skin moist and protect it from drying out. On the surface of the skin is a sebum film made of a mixture of sebum and sweat, which protects the skin from external stimuli.
・Intercellular lipids
A substance called intercellular lipid fills the space between the stratum corneum cells, which are made up of many layers.
Intercellular lipids have a layer of water and an oil layer that overlap to form a lamellar structure, which functions as a strong barrier.

reference)
"Discovery of NMF-producing enzyme and elucidation of new skin roughness mechanism"
Basic knowledge of cosmetics
- Skin structure
- How to identify your skin type
- Seasons and skin
- Sweat and odor
- Skin care basics
- Basic care steps
- Cleansing Basics
- Basics of face washing
- Basic knowledge of lotion
- Basic knowledge of beauty serums
- Cream Basics
- Sunscreen basics
- Causes of skin problems and how to care for them
- How to Find the Right Skin Care Products for You
- To soothe the skin
- Causes and Treatment of Wrinkles and Sagging Skin

